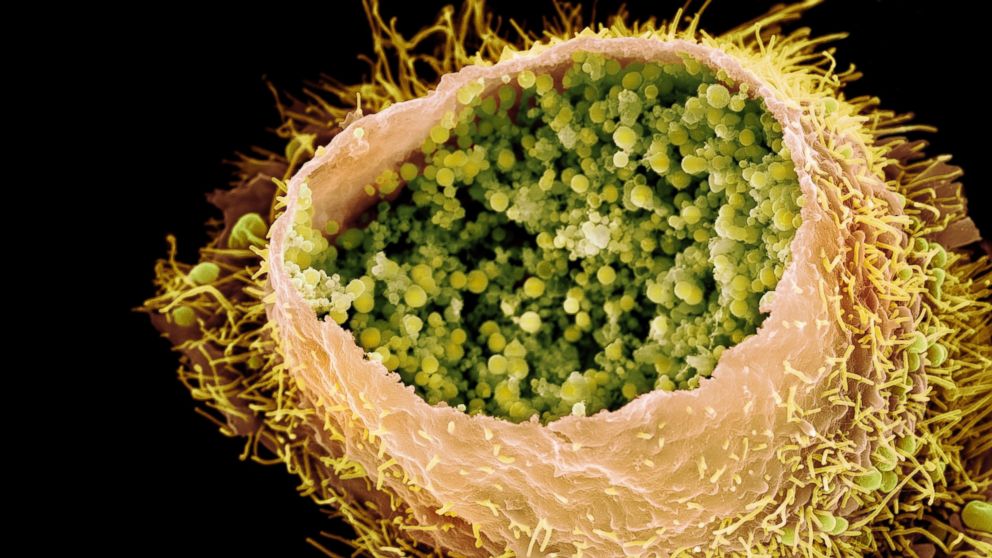
Chlamydia is a sexually transmitted infection caused by the bacterium Chlamydia trachomatis. It is one of the most common sexually transmitted infections and can affect both men and women. Chlamydia can be easily treated with antibiotics, but if left untreated, it can lead to serious health problems, such as pelvic inflammatory disease, infertility, and ectopic pregnancy in women, and epididymitis and infertility in men. Chlamydia is spread through unprotected vaginal, anal, or oral sex with an infected person. It can also be spread from mother to child during childbirth. The best way to prevent chlamydia is to practice safe sex by using condoms, getting regular STI screenings, and avoiding sexual contact with anyone who has the infection.
Chlamydia is caused by the bacterium Chlamydia trachomatis, which is spread through sexual contact with an infected person. This includes vaginal, anal, and oral sex. The bacterium can infect the cervix, urethra, rectum, and throat, as well as the eyes if they come into contact with infected genital secretions.
Chlamydia can also be spread from a pregnant woman to her baby during childbirth, which can lead to eye infections or pneumonia in the baby.
Risk factors for chlamydia infection include having unprotected sex, having multiple sexual partners, and having a history of sexually transmitted infections. However, anyone who is sexually active can become infected with chlamydia, regardless of their age or sexual orientation.
It's important to note that chlamydia can be present in the body without causing any symptoms, so someone can unknowingly transmit the infection to their sexual partner(s). This is why regular STI testing is important for sexually active individuals.
Chlamydia can be diagnosed in men through various diagnostic tests. One of the most common tests is a urine test, where a sample of urine is collected and analyzed for the presence of Chlamydia trachomatis bacteria. Another test involves taking a swab of the urethra or rectum to collect a sample for testing.
In some cases, a doctor may also perform a physical exam to look for signs of chlamydia, such as discharge from the penis, swollen or tender testicles, or rectal pain or discharge.
It's important for sexually active men to get regular STI screenings, as chlamydia can be present in the body without causing any symptoms. Left untreated, chlamydia can lead to serious health problems, such as epididymitis, which is a painful swelling of the testicles, and infertility. Treatment for chlamydia typically involves a course of antibiotics, which can effectively clear the infection.
Chlamydia can be effectively treated with antibiotics. The most commonly prescribed antibiotics for chlamydia are azithromycin and doxycycline. These medications can be taken orally, either in a single dose or over the course of several days, depending on the severity of the infection.
It's important to finish the full course of antibiotics, even if symptoms improve or go away, to ensure that the infection is completely cleared from the body. It's also recommended to abstain from sexual activity until the infection has been completely treated to avoid spreading it to sexual partners.
In addition to treating the infection, it's important for sexual partners to be tested and treated for chlamydia to prevent reinfection.
Regular STI testing is recommended for sexually active individuals to catch and treat chlamydia early, before it can lead to serious health problems. Safe sex practices, such as using condoms, can also help prevent the spread of chlamydia and other sexually transmitted infections.
